mssql_to_postgresql
- pyhelpers.dbms.mssql_to_postgresql(mssql, postgres, mssql_schema=None, postgres_schema=None, chunk_size=None, excluded_tables=None, file_tables=False, memory_threshold=2.0, update=False, confirmation_required=True, verbose=True)
Copy tables of a database from a Microsoft SQL server to a PostgreSQL server.
- Parameters
mssql (pyhelpers.dbms.MSSQL) – name of a Microsoft SQL (source) database
postgres (pyhelpers.dbms.PostgreSQL) – name of a PostgreSQL (destination) database
mssql_schema (str or None) – name of a schema to be migrated from the SQl Server
postgres_schema (str or None) – name of a schema to store the migrated data in the PostgreSQL server
chunk_size (int or None) – number of rows in each batch to be read/written at a time, defaults to
Noneexcluded_tables (list or None) – names of tables that are excluded from the data migration
file_tables (bool) – whether to include FileTables, defaults to
Falsememory_threshold (float or int) – threshold (in GiB) beyond which the data is migrated by partitions, defaults to
2.update (bool) – whether to redo the transfer between the database servers, defaults to
Falseconfirmation_required (bool) – whether asking for confirmation to proceed, defaults to
Trueverbose (bool or int) – whether to print relevant information, defaults to
True
Examples:
>>> from pyhelpers.dbms import mssql_to_postgresql, PostgreSQL, MSSQL >>> from pyhelpers._cache import example_dataframe >>> # Connect/create a PostgreSQL database, which is named [testdb] >>> mssql_testdb = MSSQL(database_name='testdb') Creating a database: [testdb] ... Done. Connecting <server_name>@localhost:1433/testdb ... Successfully. >>> mssql_testdb.database_name 'testdb' >>> example_df = example_dataframe() >>> example_df Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> test_table_name = 'example_df' >>> # Import the example dataframe into a table named [example_df] >>> mssql_testdb.import_data(example_df, table_name=test_table_name, index=True, verbose=2) To import data into [dbo].[example_df] at <server_name>@localhost:1433/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Importing the data into the table [dbo].[example_df] ... Done. >>> mssql_testdb.get_column_names(table_name=test_table_name) ['City', 'Longitude', 'Latitude']
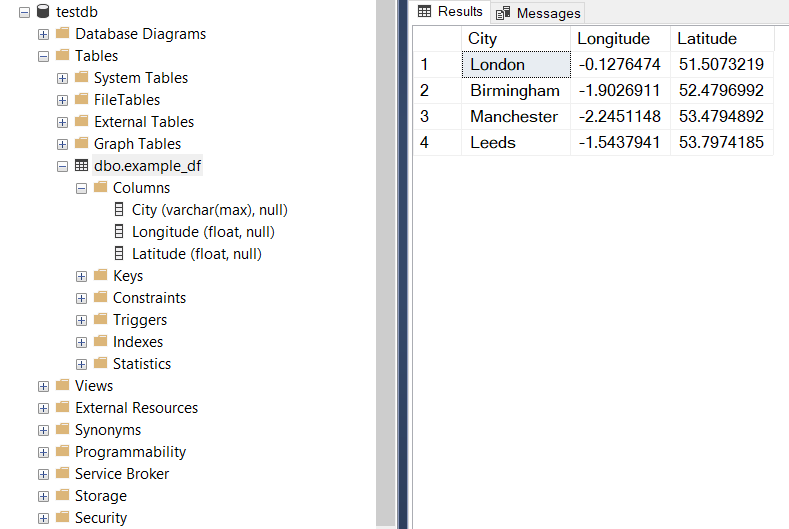
Fig. 19 The table [dbo].[example_df] in the Microsoft SQL Server database [testdb].
>>> # Create an instance for a PostgreSQL database, which is also named "testdb" >>> postgres_testdb = PostgreSQL(database_name='testdb') Password (postgres@localhost:5432): *** Creating a database: "testdb" ... Done. Connecting postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ... Successfully. >>> # For now, the newly-created database doesn't contain any tables >>> postgres_testdb.get_table_names() [] >>> # Copy the example data from the SQL Server to the PostgreSQL "testdb" (under "public") >>> mssql_to_postgresql(mssql=mssql_testdb, postgres=postgres_testdb) To copy tables from [testdb] (MSSQL) to "testdb" (PostgreSQL) ? [No]|Yes: yes Processing tables ... (1/1) Copying [dbo].[example_df] to "public"."example_df" ... Done. Completed. >>> postgres_testdb.get_table_names() ['example_df']
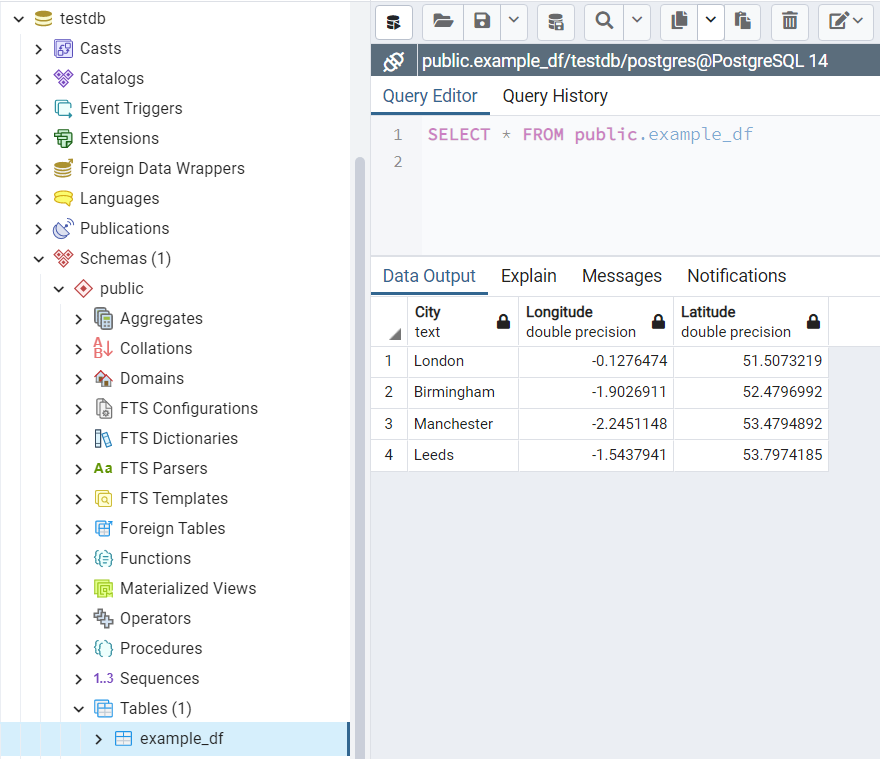
Fig. 20 The table “dbo”.”example_df” in the PostgreSQL database “testdb”.
>>> # Drop/delete the created databases >>> mssql_testdb.drop_database(verbose=True) To drop the database [testdb] from <server_name>@localhost:1433 ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping [testdb] ... Done. >>> postgres_testdb.drop_database(verbose=True) To drop the database "testdb" from postgres:***@localhost:5432 ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping "testdb" ... Done.