MSSQL.import_data
- MSSQL.import_data(data, table_name, schema_name=None, if_exists='fail', force_replace=False, chunk_size=None, col_type=None, method='multi', index=False, confirmation_required=True, verbose=False, **kwargs)
Import tabular data into a table.
See also [DBMS-MS-ID-1].
- Parameters
data (pandas.DataFrame or pandas.io.parsers.TextFileReader or list or tuple) – tabular data to be dumped into a database
table_name (str) – name of a table
schema_name (str or None) – name of a schema; when
schema_name=None(default), it defaults toDEFAULT_SCHEMA(i.e.'public')if_exists (str) – if the table already exists, to
'replace','append'or, by default,'fail'and do nothing but raise a ValueError.force_replace (bool) – whether to force replacing existing table, defaults to
Falsechunk_size (int or None) – the number of rows in each batch to be written at a time, defaults to
Nonecol_type (dict or None) – data types for columns, defaults to
Nonemethod (str or None or Callable) –
method for SQL insertion clause, defaults to
'multi'None: uses standard SQLINSERTclause (one per row);'multi': pass multiple values in a singleINSERTclause;callable (e.g.
PostgreSQL.psql_insert_copy) with signature(pd_table, conn, keys, data_iter).
index (bool) – whether to dump the index as a column
confirmation_required (bool) – whether to prompt a message for confirmation to proceed, defaults to
Trueverbose (bool or int) – whether to print relevant information in console, defaults to
Falsekwargs – [optional] parameters of pandas.DataFrame.to_sql
Examples:
>>> from pyhelpers.dbms import MSSQL >>> from pyhelpers._cache import example_dataframe >>> testdb = MSSQL(database_name='testdb') Creating a database: [testdb] ... Done. Connecting <server_name>@localhost:1433/testdb ... Successfully. >>> example_df = example_dataframe() >>> example_df Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> test_table_name = 'example_df' >>> testdb.import_data(example_df, table_name=test_table_name, index=True, verbose=2) To import data into [dbo].[example_df] at <server_name>@localhost:1433/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Importing the data into the table [dbo].[example_df] ... Done.
The imported example data can also be viewed using Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (as illustrated in Fig. 18 below):
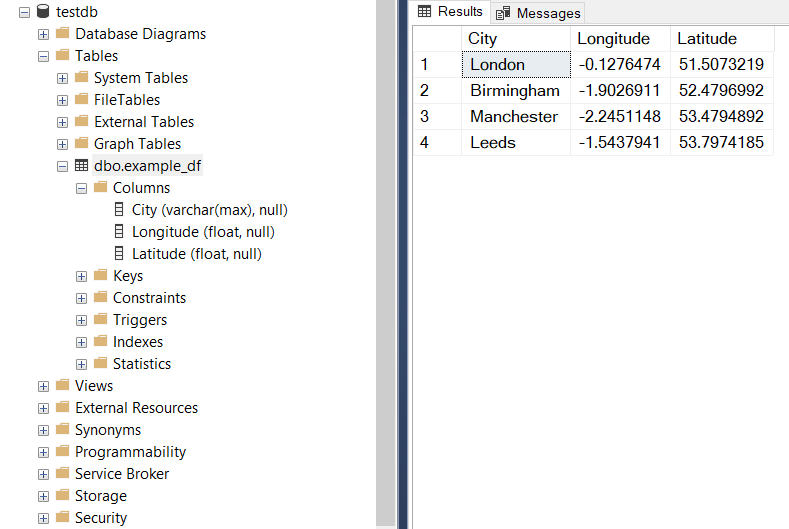
Fig. 18 The table [dbo].[example_df] in the database [testdb].
>>> # Drop/delete the table [dbo].[example_df] >>> testdb.drop_table(table_name=test_table_name, verbose=True) To drop the table [dbo].[example_df] from <server_name>@localhost:1433/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping [dbo].[example_df] ... Done. >>> # Drop/delete the database [testdb] >>> testdb.drop_database(verbose=True) To drop the database [testdb] from <server_name>@localhost:1433 ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping [testdb] ... Done.
See also
Examples for the method
MSSQL.read_table().