PostgreSQL.read_sql_query
- PostgreSQL.read_sql_query(sql_query, method='tempfile', max_size_spooled=1, delimiter=',', tempfile_kwargs=None, stringio_kwargs=None, **kwargs)
Read table data by SQL query (recommended for large table).
See also [DBMS-PS-RSQ-1], [DBMS-PS-RSQ-2] and [DBMS-PS-RSQ-3].
- Parameters
sql_query (str) – a SQL query to be executed
method (str) –
method to be used for buffering temporary data
'tempfile'(default): use tempfile.TemporaryFile'stringio': use io.StringIO'spooled': use tempfile.SpooledTemporaryFile
max_size_spooled (int or float) –
max_sizeof tempfile.SpooledTemporaryFile, defaults to1(in gigabyte)delimiter (str) – delimiter used in data, defaults to
','tempfile_kwargs (dict or None) – [optional] parameters of tempfile.TemporaryFile or tempfile.SpooledTemporaryFile
stringio_kwargs (dict or None) – [optional] parameters of io.StringIO, e.g.
initial_value(default:'')kwargs – [optional] parameters of pandas.read_csv
- Returns
data frame as queried by the statement
sql_query- Return type
pandas.DataFrame
Examples:
>>> from pyhelpers.dbms import PostgreSQL >>> from pyhelpers._cache import example_dataframe >>> testdb = PostgreSQL('localhost', 5432, 'postgres', database_name='testdb') Password (postgres@localhost:5432): *** Creating a database: "testdb" ... Done. Connecting postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ... Successfully. >>> # Create an example dataframe >>> example_df = example_dataframe() >>> example_df Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> table = 'England' >>> schema = 'points' >>> # Import the data into a table named "points"."England" >>> testdb.import_data(example_df, table, schema, index=True, verbose=2) To import data into "points"."England" at postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Creating a schema: "points" ... Done. Importing the data into the table "points"."England" ... Done.
The table “points”.”England” is illustrated in Fig. 14 below:
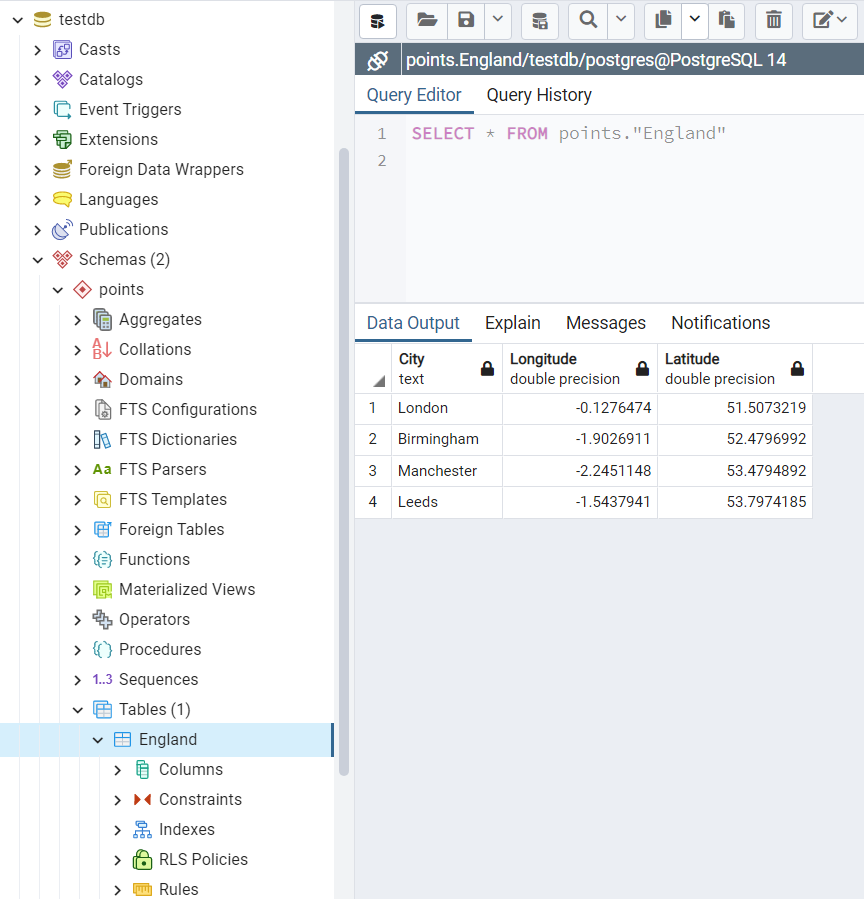
Fig. 17 The table “points”.”England” in the database “testdb”.
>>> rslt = testdb.table_exists(table_name=table, schema_name=schema) >>> print(f"The table "{schema}"."{table}" exists? {rslt}.") The table "points"."England" exists? True. >>> # Retrieve the data using the method .read_table() >>> example_df_ret = testdb.read_table(table, schema_name=schema, index_col='City') >>> example_df_ret Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> # Alternatively, read the data by a SQL query statement >>> sql_qry = f'SELECT * FROM "{schema}"."{table}"' >>> example_df_ret_alt = testdb.read_sql_query(sql_query=sql_qry, index_col='City') >>> example_df_ret_alt Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> example_df_ret.equals(example_df_ret_alt) True >>> # Delete the table "points"."England" >>> testdb.drop_table(table_name=table, schema_name=schema, verbose=True) To drop the table "points"."England" from postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping "points"."England" ... Done. >>> # Delete the schema "points" >>> testdb.drop_schema(schema_names=schema, verbose=True) To drop the schema "points" from postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping "points" ... Done. >>> # Delete the database "testdb" >>> testdb.drop_database(verbose=True) To drop the database "testdb" from postgres:***@localhost:5432 ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping "testdb" ... Done.
Aside: a brief example of using the parameter
paramsfor pandas.read_sqlimport datetime import pandas as pd sql_qry = 'SELECT * FROM "table_name" ' 'WHERE "timestamp_column_name" BETWEEN %(ts_start)s AND %(ts_end)s' params = {'d_start': datetime.datetime.today(), 'd_end': datetime.datetime.today()} data_frame = pd.read_sql(sql=sql_qry, con=testdb.engine, params=params)