PostgreSQL.get_primary_keys
- PostgreSQL.get_primary_keys(table_name, schema_name=None, names_only=True)[source]
Get the primary keys of a table.
- Parameters:
table_name (str) – name of a table
schema_name (str | None) – name of a schema, defaults to
Nonenames_only (bool) – whether to return only the names of the primary keys, defaults to
True
- Returns:
primary key(s) of the given table
- Return type:
list | pandas.DataFrame
Examples:
>>> from pyhelpers.dbms import PostgreSQL >>> from pyhelpers._cache import example_dataframe >>> testdb = PostgreSQL('localhost', 5432, 'postgres', database_name='testdb') Password (postgres@localhost:5432): *** Creating a database: "testdb" ... Done. Connecting postgres:***@localhost:5432/testdb ... Successfully. >>> dat = example_dataframe() >>> dat Longitude Latitude City London -0.127647 51.507322 Birmingham -1.902691 52.479699 Manchester -2.245115 53.479489 Leeds -1.543794 53.797418 >>> tbl_name = 'test_table' >>> testdb.import_data(data=dat, table_name=tbl_name, index=True, verbose=True) To import data into "public"."test_table" at postgres:***@localhost:5432/postgres ? [No]|Yes: yes >>> pri_keys = testdb.get_primary_keys(table_name=tbl_name) >>> pri_keys [] >>> testdb.add_primary_keys(primary_keys='City', table_name=tbl_name)
The “test_table” is illustrated in Fig. 14 below:
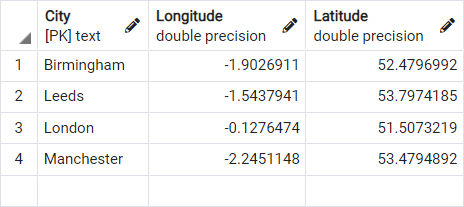
Fig. 14 The table “test_table” (with a primary key) in the database.
>>> pri_keys = testdb.get_primary_keys(table_name=tbl_name) >>> pri_keys ['City'] >>> pri_keys = testdb.get_primary_keys(table_name=tbl_name, names_only=False) >>> pri_keys key_column data_type 0 City text >>> # Delete the database "testdb" >>> testdb.drop_database(verbose=True) To drop the database "testdb" from postgres:***@localhost:5432 ? [No]|Yes: yes Dropping "testdb" ... Done.